Key takeaways
The decision on the right birth control option is deeply personal and depends on a variety of factors including health conditions, comfort with procedures, and lifestyle habits.
Birth control options range from hormonal methods like pills, implants, and shots to barrier methods such as male and female condoms, with costs varying from free to $1,300.
The most effective forms of birth control are the implant and the IUD, both over 99% effective, while options like the birth control pill are less effective due to the possibility of human error.
Non-hormonal or low-hormone options, such as copper IUDs and barrier methods, are available for those with specific health conditions or preferences, offering a wide range of choices to suit different needs.
Birth control is any type of medication, device, or method used to prevent pregnancy. Some forms of contraception are also used to treat common medical conditions. Common forms include condoms, pills, and intrauterine devices (IUDs). Some types of birth control are more effective than others.
Ultimately, the decision on what type of birth control is right for you is between you and your healthcare provider. Your ideal birth control depends on a number of factors, including whether you can or want to use hormonal methods, preferences for your menstrual cycle, how comfortable you are with small medical procedures, whether you would remember to take oral medication regularly, and more.
In this guide, we’ll explore the most common birth control methods. We’ll answer questions about the types of birth control to help you make the most informed decision regarding your contraception.
What are the different types of birth control options?
There are many forms of birth control. The most common forms of reversible birth control, according to the National Survey of Family Growth, are:
- Hormonal birth control pills
- Barrier options (e.g., male condoms, female condoms, birth control sponge)
- Intrauterine devices (aka IUDs)
- Fertility awareness-based methods
- Emergency contraception (hormonal pills and copper IUD)
- Hormonal implants
- Hormonal shots
- Hormonal patches
- Hormonal vaginal rings
Non-reversible birth control includes:
- Female permanent contraception (tubal ligation)
How much does birth control cost?
The cost of birth control varies by method, but on average, birth control can cost between $0 and $50 per month. Some birth control options, such as an IUD, can cost $1,300 for a one-time fee but will last for up to 12 years. The Affordable Care Act requires that most private plans cover contraceptive services for pregnancy capable persons without cost-sharing—this includes patient education and counseling and FDA-approved methods of contraception with a prescription. Medicaid, public insurance, Federal Title X, and some state funding programs also cover contraception without a copayment.
RELATED: How to get free birth control (even without insurance)
What is the most effective form of birth control?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the two most effective forms of birth control are hormonal implants and IUDs, which are both over 99% effective.
Other forms of birth control, such as the shot and birth control pill, boast a similar effectiveness rate with perfect use. However, the pill and other methods that are used on a schedule are less effective when the schedule isn’t strictly kept. For that reason, they’re not 99% effective with normal use.
Hormonal vs. non-hormonal birth control options
Choosing the right birth control method depends on factors like your health history, lifestyle, and personal preferences. Knowing the differences between hormonal and non-hormonal options can help you decide.
Non-hormonal birth control options
Non-hormonal birth control options are available for those who want to avoid hormones. These include:
- Copper IUDs—Use no hormones
- Barrier methods (e.g., male condoms, female condoms)—These are the only forms that also provide some protection against sexually transmitted infections.
- Fertility awareness-based methods
Hormonal birth control options
Hormonal birth control options can be categorized based on whether they contain estrogen and progestin or just progestin.
Progestin-only birth control:
- Birth control implant—progestin only, no estrogen
- Hormonal IUDs—progestin only, no estrogen
- Birth control shot—progestin only, no estrogen
- Progestin-only birth control pills, including the over-the-counter contraception pill—progestin-only, no estrogen
- Emergency contraception
Combination birth control:
- Combination birth control pills—contain both estrogen and progestin
- Hormonal patch—contains both estrogen and progestin
- Hormonal vaginal ring—contains both estrogen and progestin
Individuals with certain medical conditions may need to avoid estrogen-containing birth control methods. Those who have had previous blood clots are at a higher risk of developing clots when they use estrogen. Using estrogen if you have a history of migraines with auras may put you at a much higher risk of experiencing a stroke.
It’s critical to discuss your medical history with your provider to ensure you receive the best birth control option for your needs. Also, there is a helpful app from the CDC that can provide birth control information.
The birth control pill
The birth control pill is a commonly used hormonal contraceptive. There are several different types of birth control pills, each with varying hormone combinations and dosages to suit different needs and preferences. Each type works slightly differently, but all are designed to prevent ovulation and make it harder for sperm to reach an egg.
What is the birth control pill?
The birth control pill is a hormonal contraceptive (combined estrogen-progestin or progestin-only) that you take orally daily. Common brands include Alesse, Levlen, Ortho Tri-Cyclen, Loestrin, Ortho-Novum, Estrostep, Lessina, Levlite, Aviane, Levora, Lo Ovral, Aranelle, Natazia, Enpresse, Mircette, Apri, Yasmin, Nordette, and Yaz.
How do birth control pills work?
Hormonal birth control works by stopping ovulation. By stopping ovulation, there’s no egg available for the sperm to fertilize. Birth control pills also thicken the cervical mucus, which makes it harder for the sperm to reach the egg.
How effective are birth control pills?
When used as directed, the birth control pill is 99% effective. However, if you don’t take the pill consistently or skip days altogether, it becomes much less effective. Also, some prescription medications can reduce their effectiveness, so it is important to discuss this with your healthcare providers. Overall, with typical use, the birth control pill is about 93% effective.
How do you take birth control pills?
You take birth control pills orally (by mouth) once a day at approximately the same time. The time of day doesn’t matter, but it should be consistent. It is best to take with food to avoid nausea and stomach upset.
How long does it take for birth control pills to start working?
On average, the birth control pill takes seven days to become fully effective depending on where you are in your menstrual cycle. If you start the birth control pill on the first day of your period, however, it may kick in immediately. Birth control manufacturers recommend that you use a secondary method of contraception, such as condoms, for the first seven days.
What are the side effects of birth control pills?
Some side effects of birth control pills are:
- Nausea
- Headaches
- Breast tenderness
- Mood changes
- Spotting Between periods
- Weight gain
- Blood clots
- High blood pressure
- Vision changes
Intrauterine devices (IUD)
Though intrauterine devices have been a method of birth control since 1909, it wasn’t a commonly used method until the invention of the copper IUD in the 1960s. Today, IUDs are the most commonly used form of long-acting reversible birth control (LARC), highly effective, and very safe.
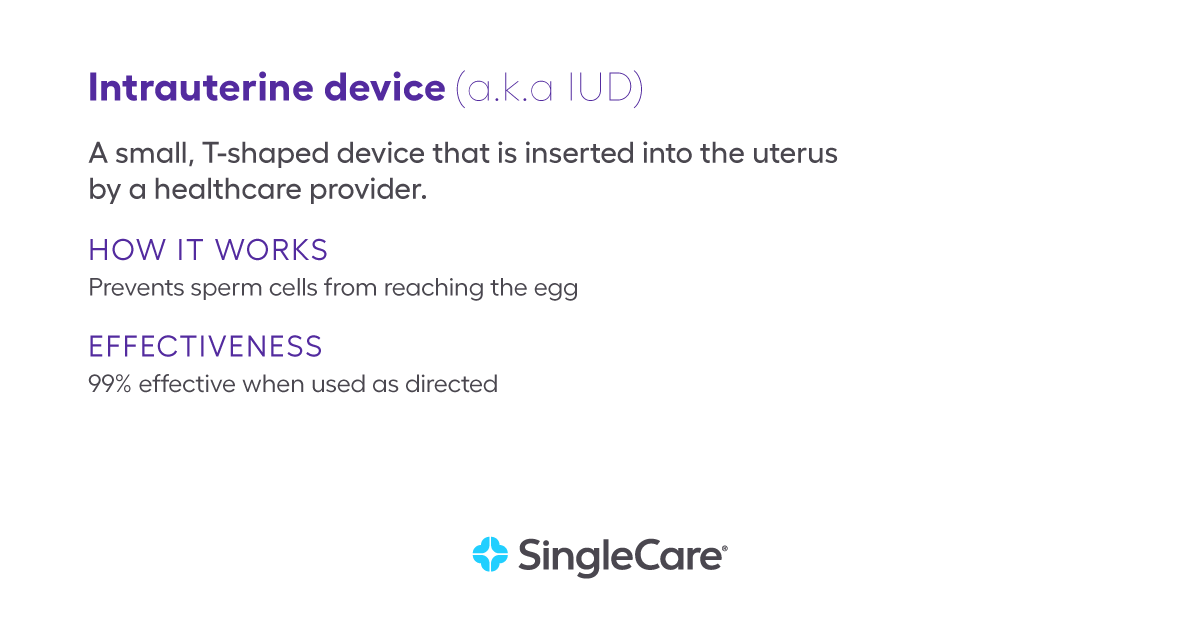
What is an IUD?
An IUD (intrauterine device) is a small, T-shaped device that is inserted into the uterus by an OB-GYN. There are two types of IUDs: progestin IUDs (Mirena, Kyleena, Liletta, and Skyla) and copper IUDs (ParaGard).
How does an IUD work?
The copper IUDs work by preventing sperm cells from reaching the egg. Sperm cells don’t react well to copper, which impedes their ability to reach the egg. Progestin IUDs thicken the mucus in the cervix and prevent ovulation (like the birth control pill).
How effective is an IUD?
An IUD is 99% effective. Since a medical professional inserts the device, there’s little risk of imperfect use as there is with the birth control pill or condoms. Copper and progestin IUDs are equally effective. However, copper IUDs have the distinction of being effective emergency contraception when inserted up to five days after unprotected sex.
How long does an IUD last?
A copper IUD is one of the longest-lasting contraceptives and is effective for up to 12 years. Depending on the IUD, progestin IUDs last between three and eight years after insertion.
How much does an IUD cost?
An IUD can be free when fully covered by insurance or cost up to $1,300 without any health insurance coverage. Most IUD websites offer discounts on copayments and charitable programs for coverage.
How long does it take an IUD to work?
A copper IUD is effective immediately after insertion as it does not rely on hormones working through your body. Hormone-based IUDs can take up to a week to become fully effective (depending on the timing of your menstrual cycle) in preventing pregnancy.
What are the side effects of IUDs?
The side effects of IUDs are listed below:
- Pain during and immediately following insertion (usually lessened when you’re on your period during insertion and if you take an ibuprofen 30 minutes before the procedure)
- Cramping and backaches in the days following insertion
- Spotting between periods
- Increasingly irregular periods (or none at all)
- In some cases, heavier periods and menstrual cramps (more common with copper IUDs)
Birth control implant
Birth control implants are an increasingly popular method of long-acting reversible birth control. Implant forms of birth control work similarly to a hormonal IUD, but it’s inserted into the arm rather than the uterus.
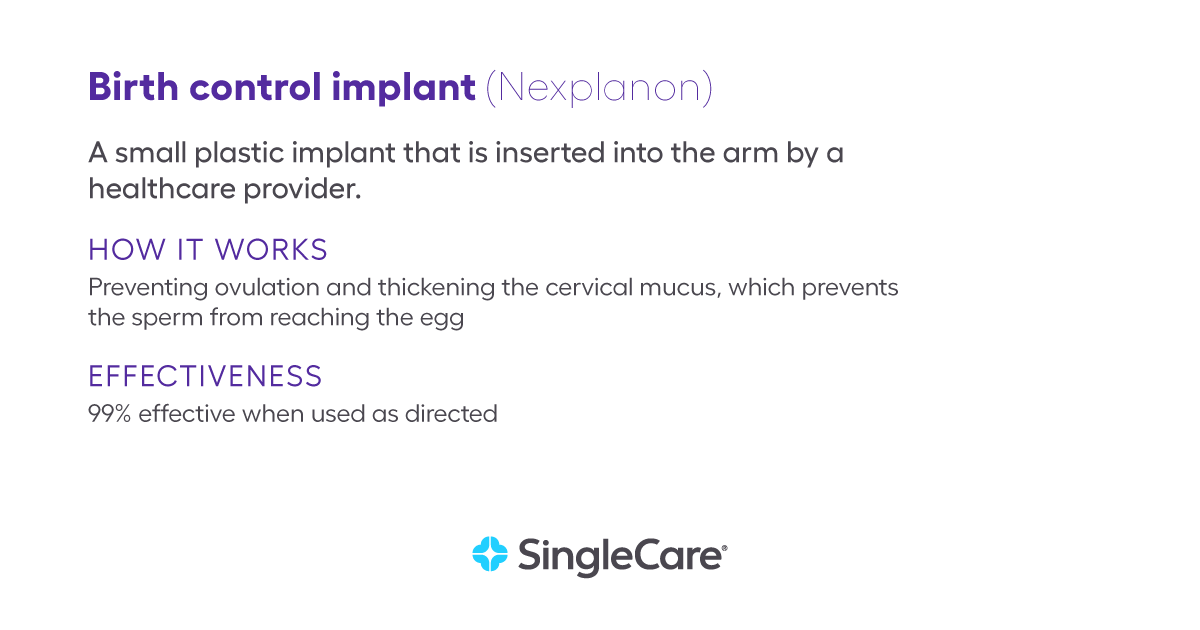
What is a birth control implant?
The birth control implant (Nexplanon) is a small plastic implant that is inserted into your arm by a trained healthcare provider during a short office visit.
How does a birth control implant work?
The birth control implant works by preventing ovulation and by thickening the cervical mucus that keeps sperm from swimming to an egg.
How effective is a birth control implant?
The birth control implant (like the IUD) is 99% effective. Unlike condoms or birth control pills, there’s almost no room for user error, which makes the birth control implant equally effective in theory and practice.
How long does a birth control implant last?
The Nexplanon is effective for up to five years. However, it can be removed early if desired.
How much does a birth control implant cost?
The birth control implant can cost as little as $0 when fully covered by insurance. It can cost up to $1,300 when not covered. Removal of the birth control implant can cost from $0 to upward of $300, depending on insurance coverage. The Nexplanon website offers information about insurance coverage.
How long does it take a birth control implant to work?
The birth control implant takes about seven days to become fully effective. However, if the implant is inserted in the first five days of your period, it might be effective at preventing pregnancy immediately.
What are the side effects of the birth control implant?
The birth control implant has several side effects to consider.
- Temporary pain at the insertion site
- Lighter or heavier periods
- No bleeding at all during your period
- Spotting between periods
- Unpredictable time between periods
- Mood swings
- Mild weight gain
- Acne
- Hair thinning
- Depression
- Headaches
Birth control shot
The birth control shot was first introduced in the late 1950s and was available as birth control in the United States starting in 1992. As a drug, it has many other uses, including easing the symptoms of menopause.
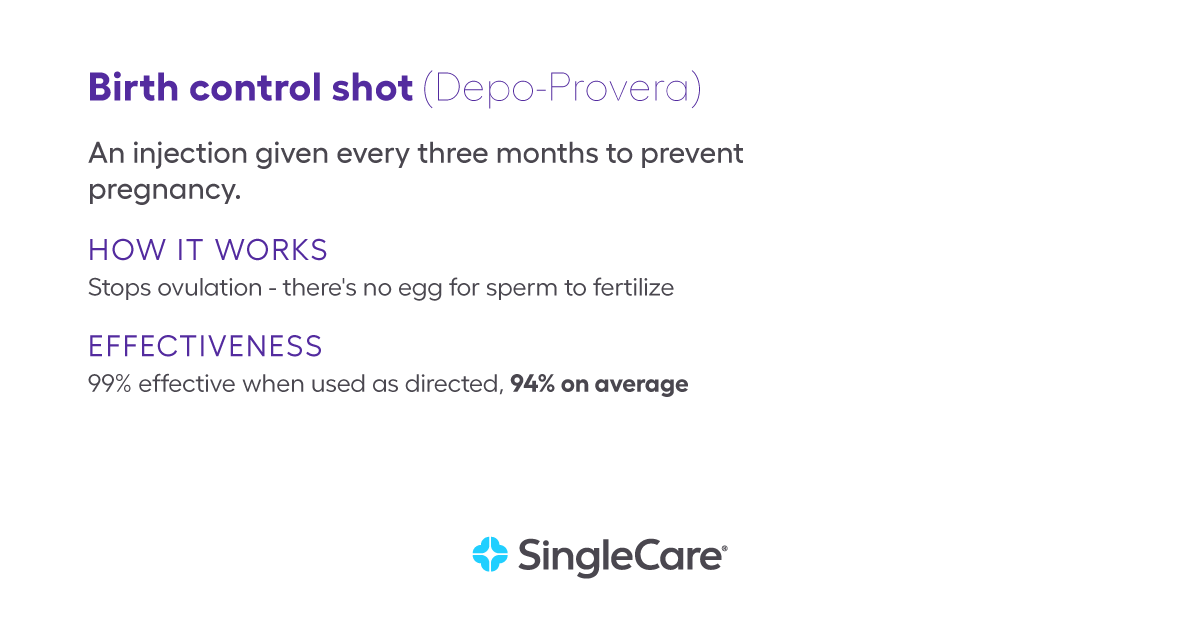
What is the birth control shot?
The birth control shot (aka Depo-Provera) is an injection given every three months to prevent pregnancy. The shot can be given by a medical professional or, in some cases, it can be administered at home. Depo-SubQ is administered under the skin (subcutaneously) rather than in the muscle (intramuscularly).
How does the birth control shot work?
Like other hormonal forms of birth control, the birth control shot works by both preventing ovulation and thickening the cervical mucus so that sperm cannot swim to eggs. The shot can be given every 10 to 15 weeks, depending on your schedule. However, manufacturers recommend getting the shot every 12 weeks because the shot is less effective when you wait more than 15 weeks between shots.
How effective is the birth control shot?
The birth control shot is 99% effective when administered on a perfect schedule. However, because shots aren’t always administered on time, the average effectiveness is 94%.
How long does the birth control shot last?
The birth control shot lasts about 12 weeks. However, it can take 10 months without shots to get pregnant. It takes time for the hormones to leave your body; however, some people are able to get pregnant immediately after the 12-week window has lapsed.
How much does the birth control shot cost?
The birth control shot can cost anywhere from $0 when fully covered by insurance to $150 per shot.
How long does it take the birth control shot to work?
After your first birth control shot, it could take up to seven days before the shot works. However, if you schedule your shot within the first five days of your period, it could be effective immediately.
What are the side effects of the birth control shot?
The birth control shot can lead to various side effects, including:
- Weight gain
- Irregular periods
- Headaches
- Mood changes
- Decreased bone density
- Nausea
- Breast tenderness
- Hair loss
- Depression
Birth control rings
The first vaginal ring, NuvaRing, was approved in 2001. It provides an alternative option for those who would prefer to avoid daily pills or more invasive methods, like contraceptive implants.
What are birth control rings?
There are three vaginal rings approved for use as hormonal contraceptives in the United States. You’ll need a prescription from a healthcare provider to use these products:
- NuvaRing, which contains etonogestrel and ethinyl estradiol (a combination of both progestin and estrogen)
- Annovera, which contains segesterone and ethinyl estradiol (an alternative progestin combined with estrogen)
- EluRyng which contains etonogestrel and ethinyl estradiol (a combination of both progestin and estrogen)
How do birth control rings work?
Vaginal rings are inserted into the vagina and continuously release hormones that are absorbed into the bloodstream. Like other hormonal options, rings work by preventing ovulation and thickening cervical mucus.
How effective are birth control rings?
All three rings are highly effective at preventing pregnancy. NuvaRing and EluRyng are 98% effective, whereas Annovera prevents pregnancy in over 97% of patients during their first year of use.
How long do birth control rings last?
All rings stay inserted for 21 days and are removed for seven days. Once removed, patients should discard a NuvaRing or EluRyng and replace it with a new ring at the start of their next cycle. However, washing an Annovera makes it suitable for reuse for up to 13 cycles.
How much do birth control rings cost?
The price of vaginal rings varies by pharmacy and insurance coverage. The cash price for a three-month supply of NuvaRing is about $525, whereas a generic version is available for about $155. Annovera is currently brand-only and available for about $2,430 for a one-year supply.
How long does it take for birth control rings to start working?
It takes about seven days for hormone levels to reach a steady state. This means it’s important to use alternate forms of birth control (like condoms) after first inserting the ring, as well as if the ring falls out and remains out for more than a few hours.
What are the side effects of birth control rings?
Individual responses to NuvaRing/EluRyng and Annovera vary due to the alternative forms of progestin. Both rings may cause the following side effects:
- Nausea
- Headache
- Tender breasts
- Abdominal pain
- Menstrual cramps
- Increased amounts of vaginal discharge
Birth control patch
The contraceptive patch is one of the newer forms of birth control. It came to market in 2002 and is popular among women who don’t want to take a daily pill and aren’t interested in long-acting reversible birth control.
What is the birth control patch?
The birth control patch is a sticker you wear on your body, much like a nicotine patch. It contains two hormones: levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol (Twirla) or norelgestromin and ethinyl estradiol (Xulane). It is often worn on the arm, lower back, or belly. The patch needs to be changed once a week. The most common brands are Xulane and Twirla.
How does the birth control patch work?
The patch, like other forms of hormonal birth control, prevents pregnancy by stopping your body from ovulating and by thickening cervical mucus that keeps sperm from meeting an egg.
How effective is the birth patch?
When the patch is used per instructions, it is 99% effective. In common use, which has some room for error, it’s approximately 91% effective. The most common error made when using the patch is not changing it regularly.
How long does the birth control patch last?
The patch lasts seven days and should be changed once a week, ideally around the same time.
How much does the birth control patch cost?
If it’s completely covered by your insurance, the patch can be free. However, it costs about $150 per prescription refill without insurance.
How long does it take the birth control patch to work?
If you start using the patch within the first five days of your period, it starts working immediately. If you start using it at any other point in your cycle, the patch could take up to seven days to start working. During these seven days, the manufacturer recommends that you use a secondary method of birth control, such as condoms.
What are the side effects of the birth control patch?
The birth control patch is another effective contraceptive option, but it may come with some side effects. The list of potential side effects include but are not limited to:
- Skin irritation
- Nausea
- Headaches
- Breast tenderness
- Mood changes
- Weight gain
- Irregular bleeding
- Dizziness
- Blood clots
Emergency contraception
Emergency contraception is a way to prevent pregnancy. There are different types of emergency contraception available, each with its own method of action and effectiveness window.
What is emergency contraception?
Emergency contraception is used to prevent pregnancy after unprotected sex or contraceptive failure, such as a broken condom or missed birth control pills. It is not intended for regular use but as a backup option to reduce the risk of unintended pregnancy.
How does emergency contraception work?
Emergency contraception works primarily by preventing or delaying ovulation if it has not already occurred. If ovulation is delayed or prevented, there is no egg available for sperm to fertilize, which means pregnancy cannot occur. There are two main types of emergency contraception hormonal pills: levonorgestrel (such as Plan B) and ulipristal acetate (ella). Levonorgestrel pills work best within 72 hours of unprotected intercourse, while ella can be taken up to five days afterward.
How effective is emergency contraception?
The effectiveness of emergency contraception depends on how quickly it is taken after unprotected sex. Levonorgestrel is most effective within the first 72 hours. Ulipristal acetate (ella) remains highly effective up to five days after intercourse. Both methods significantly reduce the risk of pregnancy but are not 100% effective.
How long does emergency contraception last?
Emergency contraception is a one-time treatment that works within hours of taking the pill. Its effects are immediate in terms of preventing ovulation, but it does not provide ongoing protection against pregnancy.
How much does emergency contraception cost?
The cost of emergency contraception varies depending on the type. Levonorgestrel pills, such as Plan B, typically cost between $40 and $50, but generic versions may be available for as little as $11. Ulipristal acetate (ella) costs around $50. Many insurance plans cover the cost of emergency contraception without a copayment if prescribed by a healthcare provider.
How long does it take emergency contraception to work?
Emergency contraception begins to work immediately upon ingestion.
What are the side effects of emergency contraception?
Emergency contraception is an important option for preventing pregnancy after unprotected sex or contraceptive failure, but it can have side effects. A list of potential side effects are:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Fatigue
- Irregular bleeding
Barrier options
Barrier options are one of the oldest forms of birth control. External (male) condoms are the most popular type of barrier birth control, but there are also internal (female) condoms, gels, spermicides, sponges, diaphragms, and cervical caps.
Condoms are the only methods of birth control in this list that protect against STDs.
How do external condoms work?
External condoms (previously known as male condoms) work by providing a barrier between the sperm and the egg. They’re worn externally on the penis and are thin, stretchy pouches that prevent semen from getting through.
How effective are external condoms?
When used perfectly, external condoms are 98% effective at preventing pregnancy. In normal use, condoms are about 85% effective. Condoms are more effective when used exactly as instructions dictate and fitted with the proper size for the penis.
How does an external condom work?
An internal (previously known as the female) condom works by acting as a barrier between the sperm and the egg during sex. Unlike the external condom, which is worn on the penis, the internal condom goes inside orifices.
How effective are internal condoms?
According to Planned Parenthood, internal condoms are 95% effective when used perfectly but are about 79% effective with normal use.
What are the side effects of condoms?
While generally safe and effective, both internal and external condoms can have some side effects:
Internal condoms:
- Vaginal irritation
- Allergic reactions
- Increased vaginal discharge
- Difficulty with insertion
External condoms:
- Skin irritation
- Allergic reactions
- Reduced sensitivity
- Breakage or slippage
How do barrier gels work?
Barrier gels, sometimes known as spermicidal gels, work by using chemicals to kill or disrupt the sperm’s ability to move, preventing them from reaching and fertilizing an egg.
Phexxi is a new non-hormonal birth control method. It is a prescription vaginal gel that prevents pregnancy by stopping sperm from reaching an egg. You insert the gel no more than one hour before intercourse. It starts working immediately and is effective for up to one hour. After sex, the gel slowly comes out of your vagina, mixed with your vaginal fluids and semen. With perfect use, Phexxi is 93% effective, but with typical use, it is about 86% effective. It does not protect against sexually transmitted infections; however, you can use it with a condom. One box (12 applications) costs around $350; however, most insurances cover it without a copayment.
What are the side effects of barrier gels?
- Vaginal burning
- Discomfort around the vaginal
- Vaginal discharge
- Vaginal itching area
- Discomfort in the genital area
- Vaginal yeast infection
- Bacterial vaginosis
- Pain while passing urine
- Allergic reactions ( lactic acid, citric acid, potassium bitartrate, or any of the ingredients)
Surgical birth control
Individuals may turn to surgical procedures for a long-term solution. These procedures include tubal ligation and vasectomy. They are generally considered non-reversible.
What is tubal ligation?
Often referred to as “getting your tubes tied,” tubal ligation involves blocking, cutting, or sealing the fallopian tubes.
How does tubal ligation work?
Tubal ligation prevents sperm from reaching an egg.
It’s important to note that this method does not prevent sexually transmitted infections.
How effective is tubal ligation?
Tubal ligation is more than 99% effective in preventing pregnancy.
How long does tubal ligation last?
Tubal ligation is a permanent method. Although an additional procedure may be able to reverse it, it is not always successful.
How much does tubal ligation cost?
This procedure is covered by most insurance plans.
How long does it take for tubal ligation to work?
Tubal ligation is effective immediately after the procedure. However, it’s important to check with your healthcare provider to confirm that the procedure was successful.
What are the side effects of tubal ligation?
Tubal ligation surgery can come with some side effects:
- Bloating
- Abdominal cramps
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Infection at the incision site
Vasectomy
What is a vasectomy?
A vasectomy is a surgical procedure that prevents sperm from being incorporated into semen.
How does a vasectomy work?
It is a form of birth control where the vas deferens are cut and sealed so that sperm cannot mix with semen during ejaculation.
A vasectomy is not effective for the control of sexually transmitted diseases.
How effective is a vasectomy?
Vasectomies are almost 100% effective at preventing pregnancy.
How long does a vasectomy last?
A vasectomy is considered a permanent method. They can sometimes be reversed through a surgical procedure called vasectomy reversal, which reconnects the vas deferens to restore the flow of sperm. The success of reversal can vary, and it may not always result in restored fertility.
How much does a vasectomy cost?
Vasectomies are covered by most insurance.
How long does it take for a vasectomy to work?
It usually takes at least two months for semen to become sperm-free after a vasectomy.
What are the side effects of a vasectomy?
Vasectomies may come with some side effects. Here are a few to be aware of:
- Pain or discomfort
- Swelling
- Bruising
- Infection
- Sperm granuloma
- Post-vasectomy pain syndrome
Natural methods of birth control
For those who would rather avoid the use of hormones or invasive methods, there are additional approaches.
Fertility awareness-based methods
Previously called “the rhythm method,” the fertility awareness method involves tracking your menstrual cycle and ovulation to determine the days you’re most likely to become pregnant. Several methods are possible, including tracking your temperature, discharge, or cycles. Tracking your fertility cycles for over a year is effective for 77% to 98% of couples.
Withdrawal method (pull-out method)
The withdrawal method is about 78% effective at preventing pregnancy. It involves pulling out the penis before ejaculation. It doesn’t prevent sexually transmitted infections.
Lactational amenorrhea method (Breastfeeding)
This is a temporary method of birth control that relies on a period of natural infertility brought on by the hormones associated with breastfeeding. This method may be effective in preventing pregnancy for about six months after giving birth, provided you have experienced no periods during this time frame. With perfect use, it is about 98% effective in preventing pregnancy but only for the first six months or when your menstrual period returns. This will not work if you are exclusively pumping breast milk.
Choosing the method that works best for you
There are many options for birth control for a reason: no single method is perfect for everyone. Many women try several different types of contraception before they find a method that works well for them.
Factors to consider
Medical history: If you have a history of smoking, cardiovascular disease, migraines, or blood clots, certain birth control options may be more dangerous. Discussing your full medical history with your healthcare providers to find an option that prioritizes your safety is important.
Convenience: Remembering to take a tablet daily may present some challenges, and missing doses can make birth control less effective. Longer-term options may be more convenient but may require a procedure to insert and remove them. Personal preferences play an important role.
Lifestyle: You may prefer a non-hormonal method, or you may have a preference for your menstrual period. Some methods may stop menstrual periods, prolong them, make them more predictable and regular, or result in unpredictable, irregular bleeding.
Price: Low-cost birth control options may be more practical, depending on your insurance coverage. Your healthcare providers will help you take costs into consideration.
Consultation with health professionals
Ultimately, your healthcare providers are your best resource. They’ll help you consider your personal needs and medical history to ensure you find an effective method to prevent pregnancy while maintaining safety. Now you know the differences between the most popular types of birth control, speak with your provider about what’s best for you.
- Birth control, CDC (2024)
- How much does birth control cost?, Investopedia (2024)
- Contraception in the United States: A closer look at experiences, preferences, and coverage, KFF (2022)
- Contraceptive use in the United States, Guttmacher (2021)
- Contraception and birth control methods, CDC (2024)
- Women’s health, National Blood Clot Alliance
- U.S. medical eligibility criteria for contraceptive use 2024, CDC (2024)
- Why birth control and migraines with aura don’t mix, Rush (2019)
- Contraception App, CDC (2024)
- Quick start algorithm for hormonal contraception, Reproductive Health Access Program (2021)
- Birth control pills, Cleveland Clinic (2023)
- IUD information, Reproductive Health Access Program (2021)
- What are hormonal IUDs?, Planned Parenthood
- Get to know the details on Mirena, Mirena (2022)
- Mirena cost and insurance support, Mirena (2023)
- Birth control implant, Planned Parenthood (2024)
- What is Nexplanon, Nexplanon (2024)
- Important information for you to know about taking ella, Ella
- Internal condom, Planned Parenthood (2024)
- Sterilization, Planned Parenthood (2024)
- Tubal ligation, Cleveland Clinic (2023)
- Vasectomy, Planned Parenthood (2024)
- Vasectomy Reversal, Johns Hopkins Medicine (2024)
- Fertility awareness, Planned Parenthood (2024)
- Withdrawal (pull out method), Planned Parenthood (2024)
- Lactation amenorrhea method (LAM), MyHealth Alberta (2023)
- Breastfeeding, Planned Parenthood (2024)